Chapter 16: Elastography
465
16
Where E isYoung’s modulus,G is the shear modulus and D= 2(1+ν)
where ν is the Poisson’s ratio. The Poisson’s ratio is the negative
value of the ratio of lateral to axial strain caused by compression or
stretching of a material. The Poisson’s ratio usually ranges between
0 and 0.5 with a perfectly incompressible material having a ratio
of 0.5. The constant D is usually close to 3 for biological tissues.
KEY CONCEPT
8.3 Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging (ARFI)
For dynamic elastogram generation, the external push or vibration
can come froman external vibration device such as a pistonmounted
transducer, seen in
Figure 15
. Or it may come from a stronger
ultrasound pulse which compresses the tissue enough to produce
measurable shear waves.
Fig. 15
A. Fibroscan transducer diagram. B. The transducer
in operation measuring liver stiffness via an intercostal approach
(B).
(Image A. Modified from Echosens and B. from
internalmedicinenews.com)
This technique is calledAcoustic Radiation Force Impulse imaging or
ARFI imaging.
2
The ARFI pulse may be used to create a static elas-
togram by imaging the strain caused by the push pulse or assessing
stiffness in a region of interest if the shear wave speed is estimated
after applying the push pulse (ARFI shear wave velocity estimate).
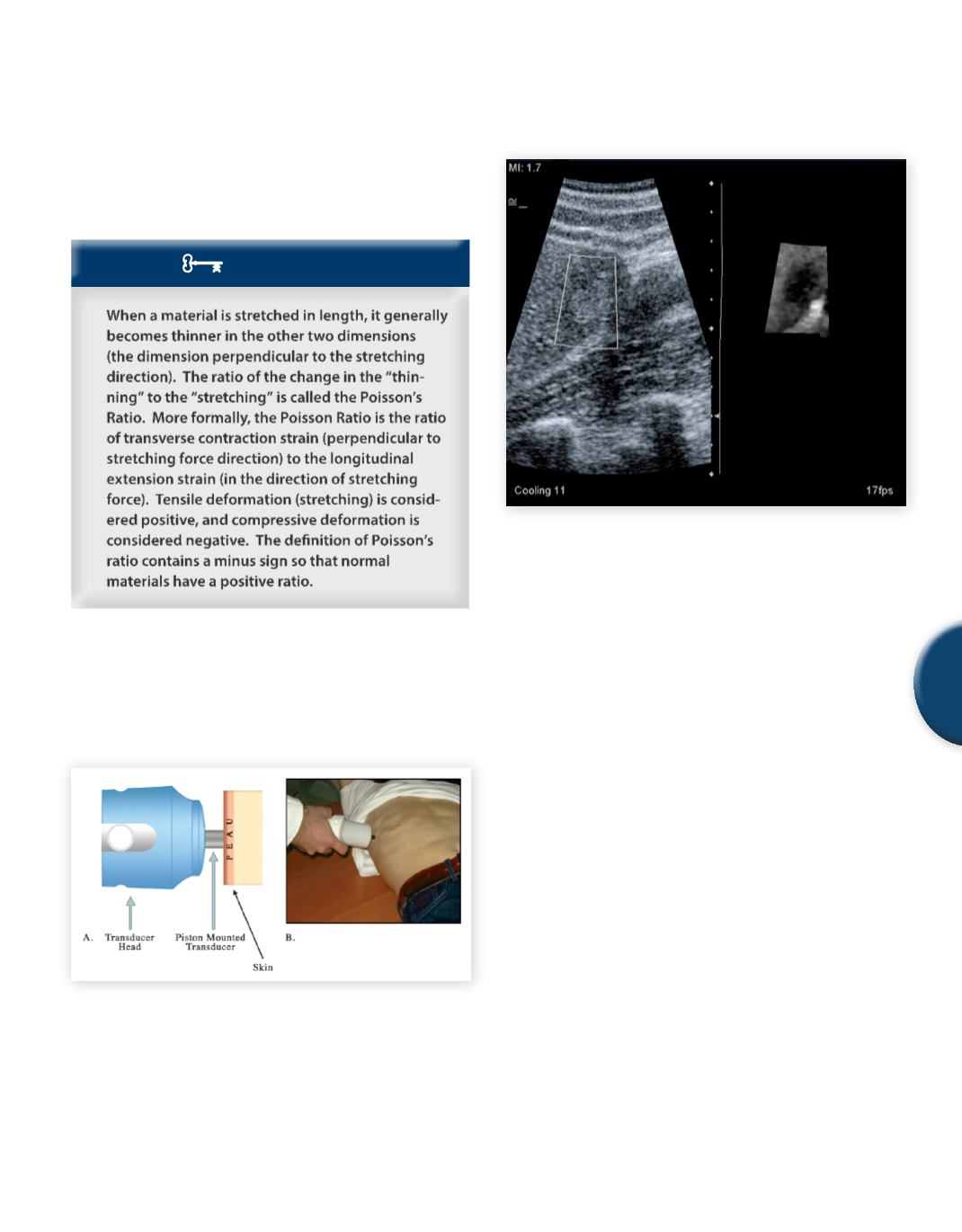
Fig. 16
ARFI Imaging of an echogenic liver mass. The acoustic
radiation force impulse creates a small amount of displacement
that can be used to generate a strain image (small image on the
right).
Although widely available outside of the United States, as of this
printing,no ultrasound devices are yet allowed to display shear wave
velocity in this country.This restriction is partly due to uncertainties
about the accuracy of the shear wave velocity estimates and partly
due to questions about the biological effects of the push pulse used
in ARFI devices. A disadvantage of the ARFI methods is depth
limitation. Due to attenuation losses, beyond a certain depth the
push pulse becomes too weak to produce measurable shear waves.
With current implementations, the maximum depth for stiffness
estimation using ARFI is about 6 cm.
8.4 Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE)
Shear wave imaging and velocity estimation can also be performed
using MRI. This method, called magnetic resonance elastography
(MRE), is available at a few medical centers in the United States.
For MRE, a non-ferrous external vibration device is needed along
with special software. The cost of MRI time may severely limit
the use of MRE, especially if ultrasound systems with comparable
capability are available.
8.5 Poroelastography
As with any new imaging technique, new variants with potential
diagnostic utility are emerging all the time. One method called po-
roelastography creates images that reflect fluidmovement in tissues.
In this method, tissue is modeled as a porous material containing
fluid. Pressure on the tissue causes shifting of fluid away from the
SAMPLE PAGE


