Chapter 3: Attenuation
67
3
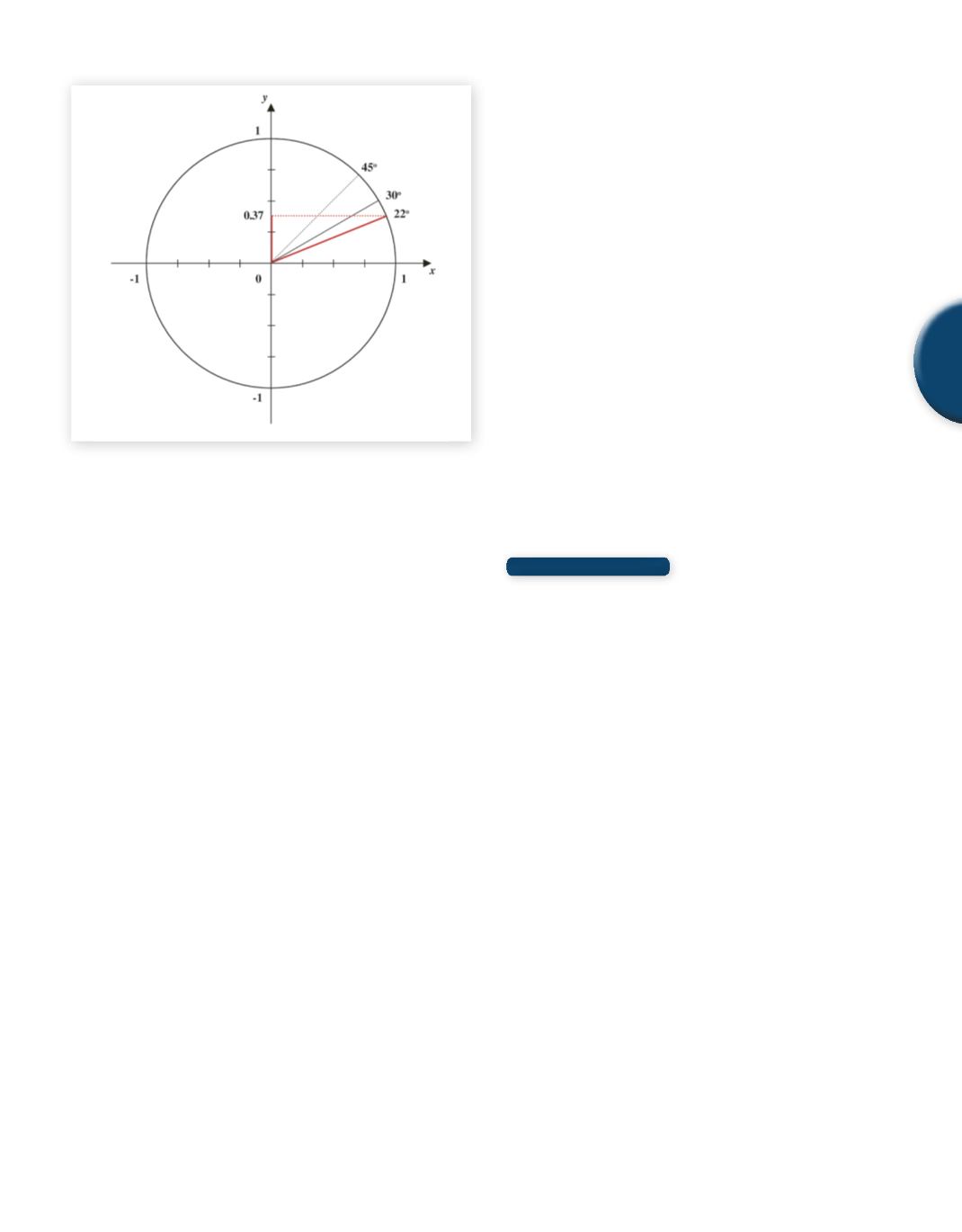
Fig. 34
Estimating the angle with a sine of 0.37
Imagine how disconcerting total internal reflection can be. If the
angle between the ultrasound beamdirection and a structure in the
body is far enough away from perpendicular, no ultrasound energy
or little ultrasound energy travels distal to that interface. The result,
as already explained, is that structures can be drawn at incorrect
locations or acoustic shadowing in the ultrasound image. This is
one of the principal reasons that 2D, or B-Mode imaging, is best
performed with the incident beam perpendicular to the structure.
This same artifact can also cause spectral and color Doppler signals
to drop out. As always, you must assess the angle between specular
reflectors and the incident beam to determine the likelihood and
type of artifact which can exist.
Note: The critical angle has been reached when the calculated
transmitted angle is 90
°
.
10.4 Important Points about Refraction
1.
The incident angle is measured relative to the (normal) line
perpendicular to the interface.
2.
There is no refraction if the ultrasound beam has normal
incidence (the beam direction is perpendicular, orthogonal,
or 90º degrees) to the interface between two media.
3.
A perpendicular beam implies that the incident angle is 0°.
4.
There is no refraction if there is no change in propagation
velocity across the interface of two media.
5.
As the difference in propagation speeds increases, and as the
angle gets further away from normal incidence, the amount
of refraction increases.
6.
There is an angle of incidence at which there is no transmission
and 100% internal reflection occurs. This angle is called the
critical angle.
7.
At the critical angle, the transmission angle is 90°.
8.
Refraction is considered an artifact which can cause objects to
be drawn at the wrong location (primarily laterally displaced)
or not even drawn at all.
9.
Refraction can cause loss of signal strength,and cause acoustic
shadows in a 2D image.
10. Refraction can also cause a loss of Doppler signal strength,and
at the critical angle, can even make the Doppler spectrum or
color Doppler disappear.
11. Exercises and Conceptual Questions
Answers Pg. 548
1.
What are the three mechanical wave interactions with the
medium which constitute attenuation?
______________________
______________________
______________________
2.
Absorption is the conversion of energy from an acoustic
wave to _______________ .
3.
Absorption (increases / decreases) with increasing frequency.
4.
Of the three interactions which constitute attenuation,
which is the dominant factor in soft tissue?
5.
What law tells at what angle an incident beam will be
transmitted?
6.
Normal incidence implies that the incident beam direction
is _______________ to the media interface.
a) parallel
b) perpendicular
c) obtuse
d) oblique
SAMPLE PAGE


