94
Level 2
Board Level
not in four discrete steps, so there are no major discontinuities as
in the figure drawn.
Fig. 28
Dynamic frequency tuning
Harmonic Imaging
Third, broad bandwidth is useful for harmonic imaging. As will be
discussed in Chapter 10, in second harmonic imaging, the trans-
mit is performed at the fundamental frequency and the receive is
performed at twice the fundamental frequency. This can obviously
only be achieved if the transducer has enough bandwidth to operate
proficiently at both of those frequencies.
Fig. 29
Use of bandwidth for harmonic imaging
Frequency Fusion (Frequency Compounding)
Fourth, broad bandwidth is useful to allow for many different types
of parallel processing techniques. These techniques typically involve
transmitting over a broad range of frequencies and then receiving
and processing the beam at two or more different narrower fre-
quency bands. The different frequency bands are each processed
to produce images which are then fused together. This technique
can therefore result in better overall image quality.
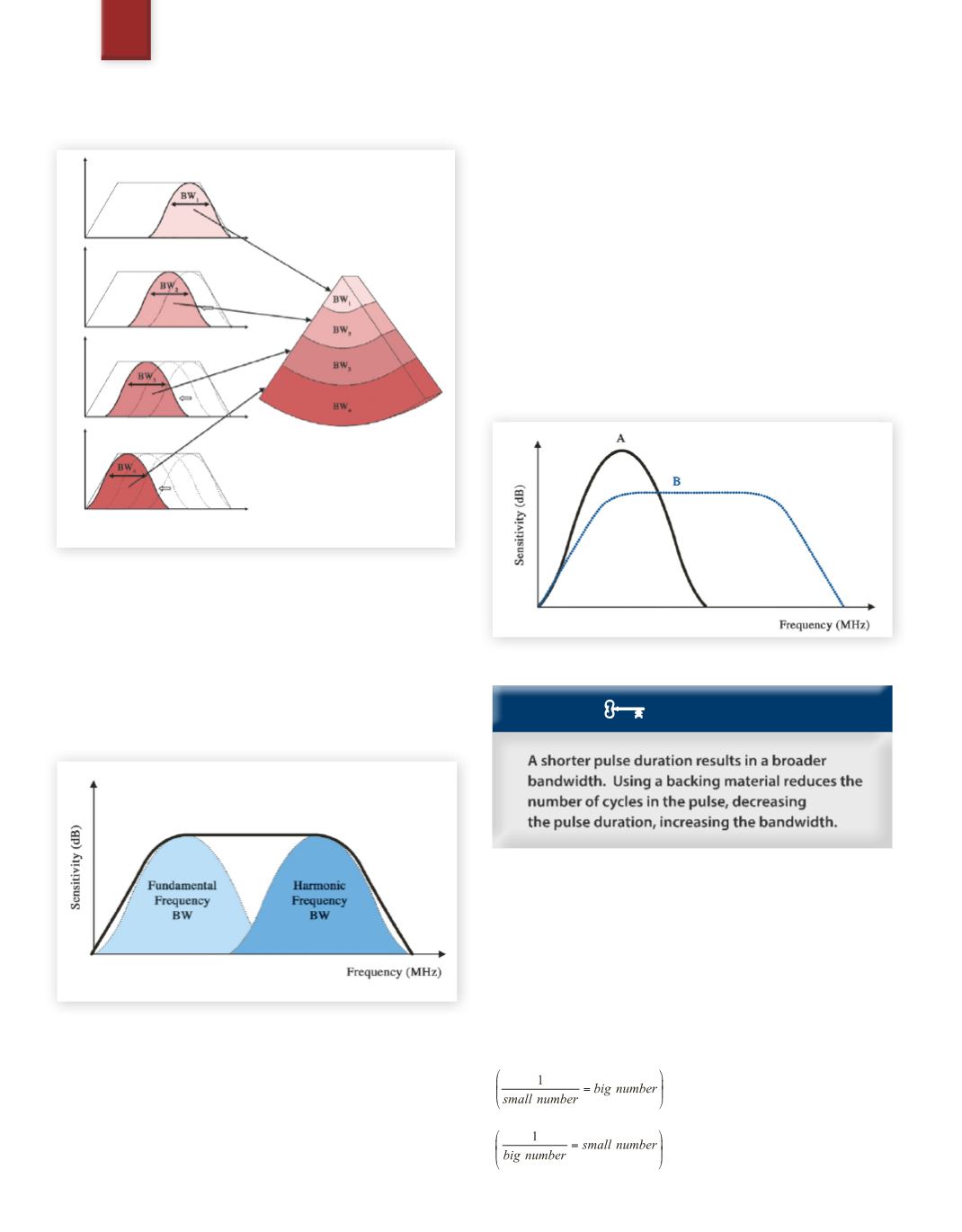
CWDoppler and Bandwidth
Is there ever a time whenmore bandwidth is not helpful? The answer
is yes. As you will see in section 16, CWDoppler requires very little
bandwidth. Therefore, if given a choice (as in
Figure 30
) between a
narrower bandwidth and more sensitivity (A), or a broader band-
width and less sensitivity (B),the more sensitive transducerAwould
be much better for CW Doppler. Also, which of the two transducer
designs would you believe to be better when penetration is needed?
Although transducer A has less bandwidth, at low frequencies there
is significantly better penetration. Since high frequency energy
does not help with penetration, transducer A is clearly better in
this case as well.
Fig. 30
More bandwidth is not always better
KEY CONCEPT
15. Pulse Duration (Width) vs. Bandwidth
15.1 The Reciprocal Relationship
We have already learned that time and frequency have a reciprocal
relationship. A long time corresponds to a low frequency and a short
time corresponds to a high frequency.
If the impulse response of a transducer is short (short pulse
duration), the transducer will have a wide bandwidth:
. If the impulse response of the
transducer is long, the transducer will have a narrow bandwidth:
. The following figure demonstrates
SAMPLE PAGE


